GLBRC Data Sets
Highlighted below are a variety of published studies that include data sets that might be of interest to the scientific community and have been deposited in online data repositories. Only data sets published in GLBRC-approved repositories following the FAIR Guiding Principles are highlighted. More information can be found on our guidelines page.
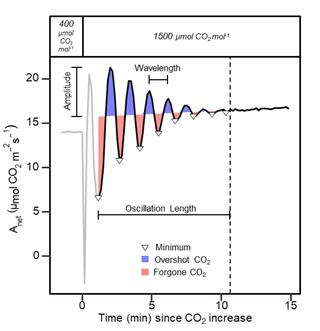
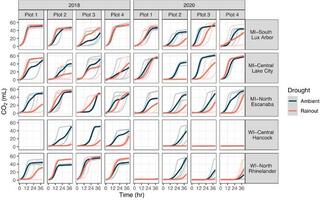
The Dynamic Assimilation Technique measures photosynthetic CO2 response curves with similar fidelity as steady-state approaches in half the time
The net CO2 assimilation (A) response to intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) is a fundamental measurement in photosynthesis and plant physiology research. The conventional A/Ci protocols rely on steady-state measurements and take 15-40 minute per measurement, limiting data resolution or biological replication.
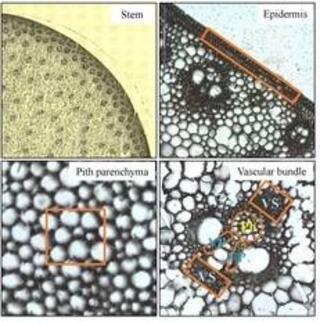
Cell-type-specific transcriptomics uncovers spatial regulatory networks in bioenergy sorghum stems
Bioenergy sorghum is a low-input, drought-resilient, deep-rooting annual crop that has high biomass yield potential enabling the sustainable production of biofuels, biopower, and bioproducts. Bioenergy sorghum's 4-5 m stems account for ~80% of the harvested biomass.
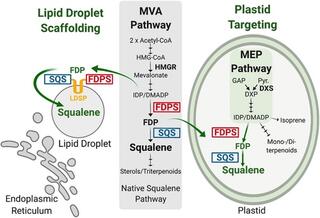
Engineered poplar for bioproduction of the triterpene squalene
Building sustainable platforms to produce biofuels and specialty chemicals has become an increasingly important strategy to supplement and replace fossil fuels and petrochemical-derived products. Terpenoids are the most diverse class of natural products that have many commercial roles as specialty chemicals.
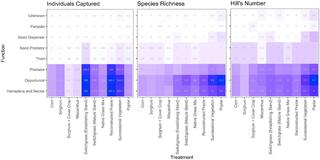
Bioenergy cropping systems shape ant community composition and functional roles
The adoption of biomass crops grown for energy is a likely source of major landscape change in coming decades during the transition from fossil fuels. There are a wide range of cropping systems that have not been widely deployed yet but could become commonplace, and our knowledge of their ecological attributes and biodiversity impacts is limited.
High temperatures and low soil moisture synergistically reduce switchgrass yields from marginal field sites and inhibit fermentation
‘Marginal lands’ are low productivity sites abandoned from agriculture for reasons such as low or high soil water content, challenging topography, or nutrient deficiency.
Self-driving laboratories to autonomously navigate the protein fitness landscape
Protein engineering has nearly limitless applications across chemistry, energy and medicine, but creating new proteins with improved or novel functions remains slow, labor-intensive and inefficient. Here we present the Self-driving Autonomous Machines for Protein Landscape Exploration (SAMPLE) platform for fully autonomous protein engineering.
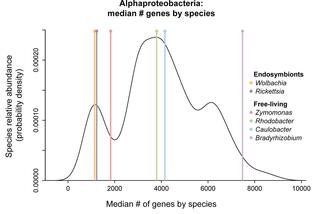
The genetics of aerotolerant growth in an alphaproteobacterium with a naturally reduced genome
Reduced genome bacteria are genetically simplified systems that facilitate biological study and industrial use. The free-living alphaproteobacterium Zymomonas mobilis has a naturally reduced genome containing fewer than 2,000 protein-coding genes. Despite its small genome, Z. mobilis thrives in diverse conditions including the presence or absence of atmospheric oxygen.
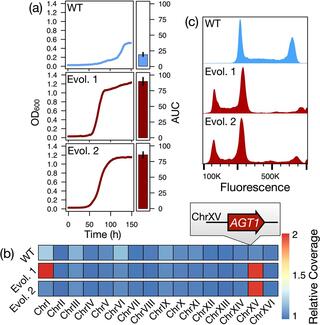
Ploidy evolution in a wild yeast is linked to an interaction between cell type and metabolism
Ploidy is an evolutionarily labile trait, and its variation across the tree of life has profound impacts on evolutionary trajectories and life histories. The immediate consequences and molecular causes of ploidy variation on organismal fitness are frequently less clear, although extreme mating type skews in some fungi hint at links between cell type and adaptive traits.
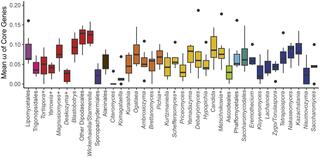
Mitochondrial genome diversity across the subphylum Saccharomycotina
Comparison of 353 yeast mitochondrial genomes revealed that, while size and GC content were fairly consistent across species, those in the genera Metschnikowia and Saccharomyces trended larger, while several species in the order Saccharomycetales, which includes S. cerevisiae, exhibited lower GC content.
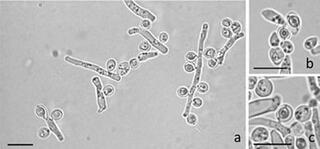
Taxogenomic analysis of a novel yeast species isolated from soil, Pichia galeolata sp. nov
A novel budding yeast species was isolated from a soil sample collected in the United States of America. Phylogenetic analyses of multiple loci and phylogenomic analyses conclusively placed the species within the genus Pichia.
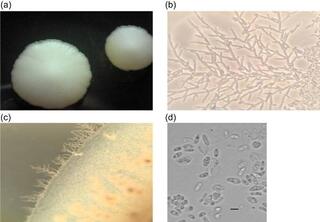
Saccharomycopsis praedatoria sp. nov., a predacious yeast isolated from soil and rotten wood in an Amazonian rainforest biome
Three yeast isolates were obtained from soil and rotting wood samples collected in an Amazonian rainforest biome in Brazil. Comparison of the intergenic spacer 5.8S region and the D1/D2 domains of the large subunit rRNA gene showed that the isolates represent a novel species of the genus Saccharomycopsis.
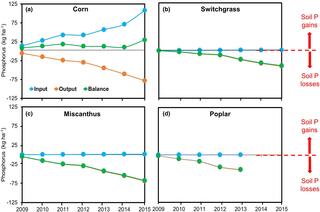
Soil phosphorus drawdown by perennial bioenergy cropping systems in the Midwestern US
Without fertilization, harvest of perennial bioenergy cropping systems diminishes soil nutrient stocks, yet the time course of nutrient drawdown has not often been investigated.
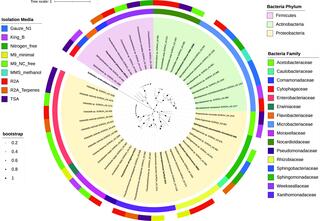
Genome-sequenced bacterial collection from sorghum epicuticular wax
A collection of 44 isolates isolated from the epicuticular wax of stems of energy sorghum is available at the Great Lakes Bioenergy Researcher Center, Michigan State University, MI, USA. We enriched bacteria with putative plant-beneficial phenotypes and include information on their phenotypic diversity, taxonomy, and whole-genome sequences.
Genome-sequenced bacterial collection from sorghum aerial root mucilage
A collection of 47 bacteria isolated from the mucilage of aerial roots of energy sorghum is available at the Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center, Michigan State University, Michigan, USA. We enriched bacteria with putative plant-beneficial phenotypes and included information on phenotypic diversity, taxonomy, and whole genome sequences.
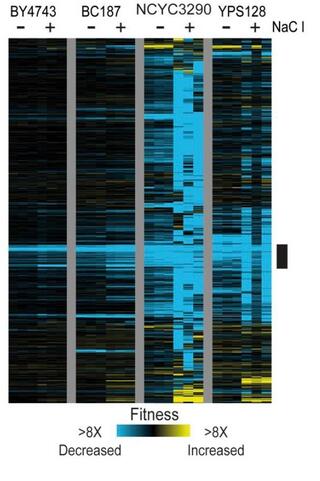
Gene-by-environment interactions influence the fitness cost of gene copy-number variation in yeast
Variation in gene copy number can alter gene expression and influence downstream phenotypes; thus copy-number variation (CNV) provides a route for rapid evolution if the benefits outweigh the cost.
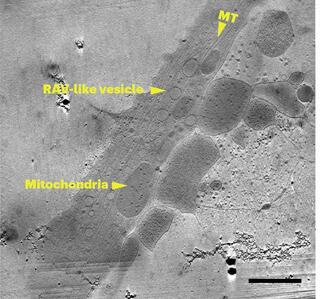
Correlative montage parallel array cryo-tomography for in situ structural cell biology
Imaging large fields of view while preserving high-resolution structural information remains a challenge in low-dose cryo-electron tomography. Here we present robust tools for montage parallel array cryo-tomography (MPACT) tailored for vitrified specimens.
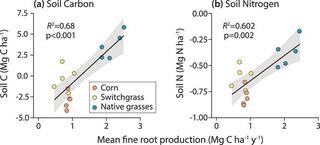
Long-term changes in soil carbon and nitrogen fractions in switchgrass, native grasses, and no-till corn bioenergy production system
Cellulosic bioenergy is a primary land-based climate mitigation strategy, with soil carbon (C) storage and nitrogen (N) conservation as important mitigation elements. Here, we present 13 years of soil C and N change under three cellulosic cropping systems: monoculture switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.), a five native grasses polyculture, and no-till corn (Zea mays L.).
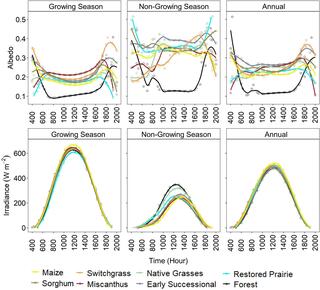
Climate cooling benefits of cellulosic bioenergy crops from elevated albedo
Changes in land surface albedo can alter ecosystem energy balance and potentially influence climate.
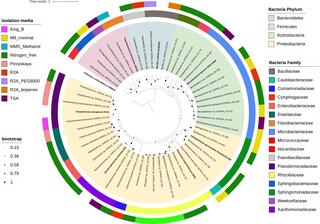
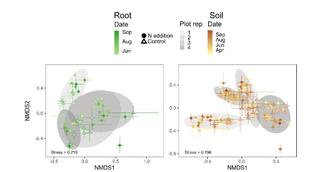
Regional biogeography versus intra-annual dynamics of the root and soil microbiome
Root and soil microbial communities constitute the below-ground plant microbiome, are drivers of nutrient cycling, and affect plant productivity. However, our understanding of their spatiotemporal patterns is confounded by exogenous factors that covary spatially, such as changes in host plant species, climate, and edaphic factors.
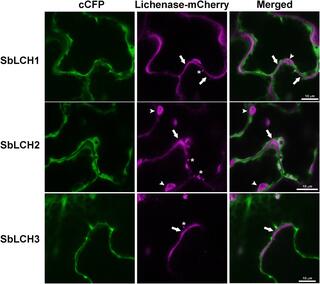
Cell- and development-specific degradation controls the levels of mixed-linkage glucan in sorghum leaves
Mixed-linkage glucan (MLG) is a component of the cell wall (CW) of grasses and is composed of glucose monomers linked by beta-1,3 and beta-1,4 bonds. MLG is believed to have several biological functions, such as the mobilizable storage of carbohydrates and structural support of the CW.