GLBRC Data Sets
Highlighted below are a variety of published studies that include data sets that might be of interest to the scientific community and have been deposited in online data repositories. Only data sets published in GLBRC-approved repositories following the FAIR Guiding Principles are highlighted. More information can be found on our guidelines page.
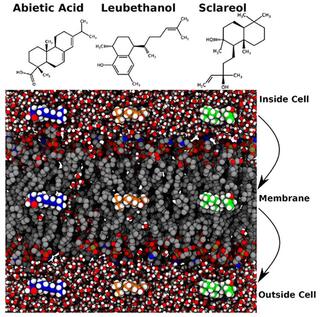
Plant terpenoid permeability through biological membranes explored via molecular simulations
Plants synthesize small molecule diterpenes composed of 20 carbons from precursor isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl disphosphate, manufacturing diverse compounds used for defense, signaling, and other functions. Industrially, diterpenes are used as natural aromas and flavoring, as pharmaceuticals, and as natural insecticides or repellents.
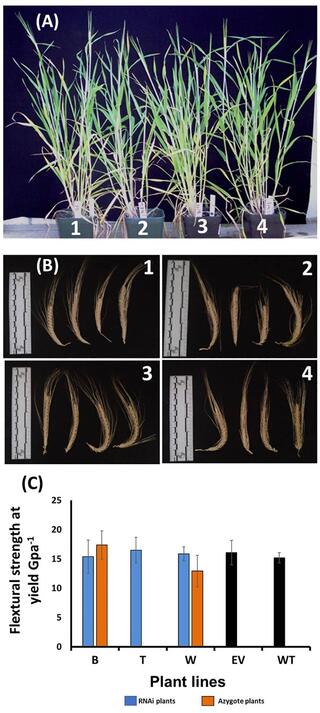
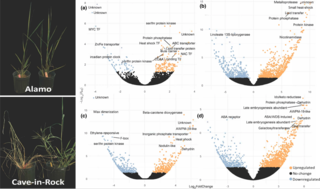
Downregulation of barley ferulate 5-hydroxylase dramatically alters straw lignin structure without impact on mechanical properties
Barley is a major cereal crop for temperate climates, and a diploid genetic model for polyploid wheat. Cereal straw biomass is an attractive source of feedstock for green technologies but lignin, a key determinant of feedstock recalcitrance, complicates bio-conversion processes. However, manipulating lignin content to improve the conversion process could negatively affect agronomic traits.
Pest suppression potential varies across 10 bioenergy cropping systems
Top-down suppression of herbivores is a fundamental ecological process and a critical service in agricultural landscapes. Adoption of bioenergy cropping systems is likely to become an increasingly important driver causing loss or gain of this service in coming decades.
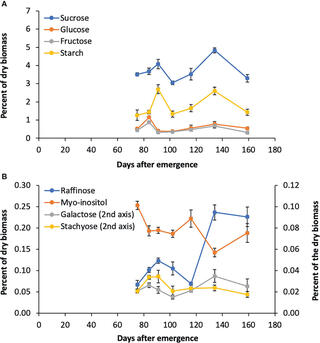
Transcriptional regulation of the raffinose family oligosaccharides pathway in Sorghum bicolor reveals potential roles in leaf sucrose transport and stem sucrose accumulation
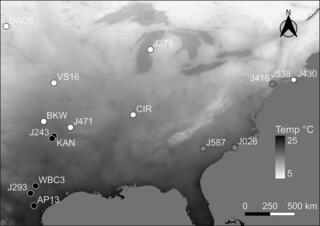
Cold acclimation threshold induction temperatures of switchgrass ecotypes grown under a long and short photoperiod
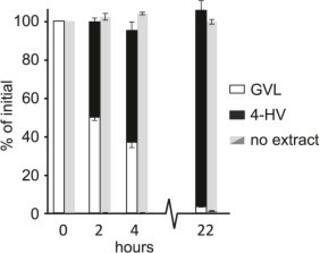
A broad specificity β-propeller enzyme from Rhodopseudomonas palustris that hydrolyzes many lactones including γ-valerolactone
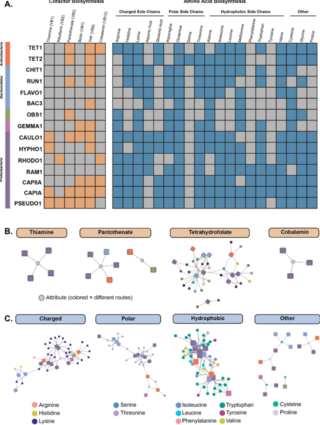
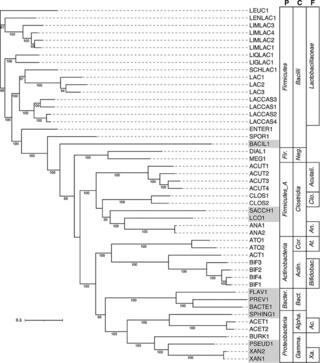
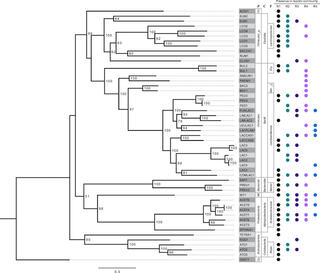
TbasCO: trait-based comparative ‘omics identifies ecosystem-level and niche-differentiating adaptations of an engineered microbiome
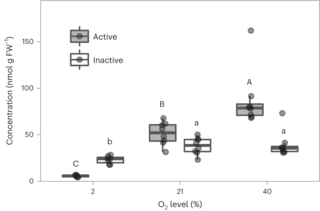
Integrated flux and pool size analysis in plant central metabolism reveals unique roles of glycine and serine during photorespiration
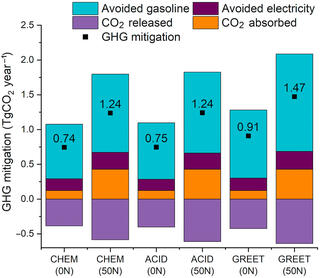
Global warming intensity of biofuel derived from switchgrass grown on marginal land in Michigan
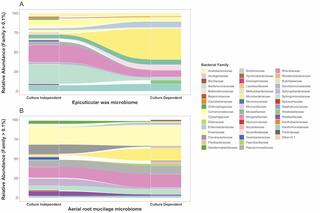
Phyllosphere exudates select for distinct microbiome members in sorghum epicuticular wax and aerial root mucilage
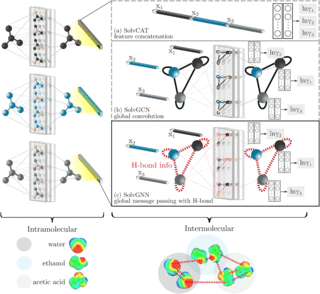
Capturing molecular interactions in graph neural networks: a case study in multi-component phase equilibrium
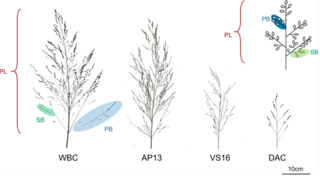
The genetic basis for panicle trait variation in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum)
Comparative transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal specialized metabolite drought stress responses in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum)
Metagenome-assembled genomes from a microbiome grown in dairy manure hydrolysate
Anaerobic microbiomes can be used to recover the chemical energy in agroindustrial and municipal wastes as useful products. Here, we report a total of 109 draft metagenome-assembled genomes from a bioreactor-fed carbohydrate-rich dairy manure hydrolysate.
Metagenomes and metagenome-assembled genomes from microbiomes metabolizing thin stillage from an ethanol biorefinery
Here, we report the metagenomes from five anaerobic bioreactors, operated under different conditions, that were fed carbohydrate-rich thin stillage from a corn starch ethanol plant. The putative functions of the abundant taxa identified here will inform future studies of microbial communities involved in valorizing this and other low-value agroindustrial residues.
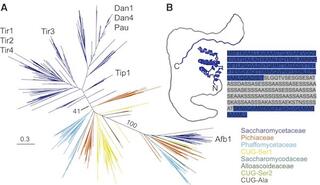
Functional divergence in a multi-gene family is a key evolutionary innovation for anaerobic growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
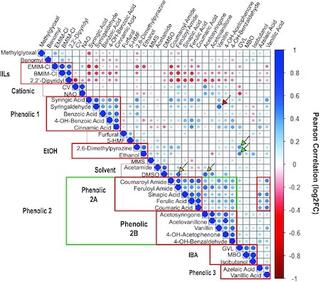
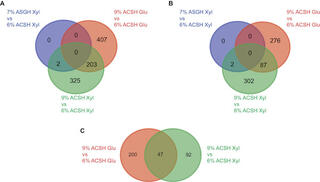
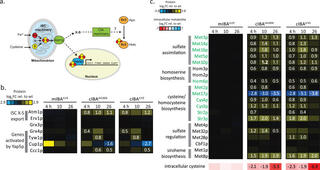
Comparative chemical genomic profiling across plant-based hydrolysate toxins reveals widespread antagonism in fitness contributions
Host genotype controls ecological change in the leaf fungal microbiome
Leaf fungal microbiomes can be fundamental drivers of host plant success, as they contain pathogens that devastate crop plants and taxa that enhance nutrient uptake, discourage herbivory, and antagonize pathogens. We measured leaf fungal diversity with amplicon sequencing across an entire growing season in a diversity panel of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum).
Transcriptomic data sets for Zymomonas mobilis 2032 during fermentation of Ammonia Fiber Expansion (AFEX)-Pretreated corn stover and switchgrass hydrolysates
The transcriptomes of Zymomonas mobilis 2032 were captured during the fermentation of ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX)-pretreated corn stover and switchgrass hydrolysates containing different concentrations of glucose and xylose. RNA samples were collected when Z. mobilis was fermenting glucose or xylose.