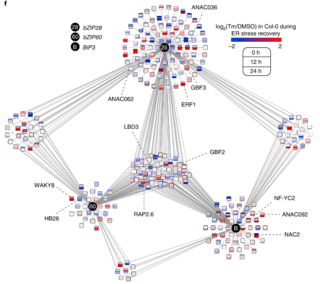
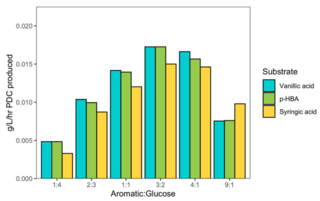
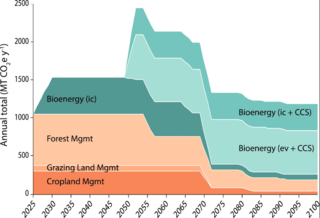
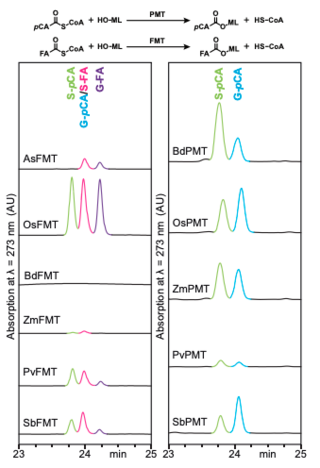
GLBRC Data Sets
Highlighted below are a variety of published studies that include data sets that might be of interest to the scientific community and have been deposited in online data repositories. Only data sets published in GLBRC-approved repositories following the FAIR Guiding Principles are highlighted. More information can be found on our guidelines page.
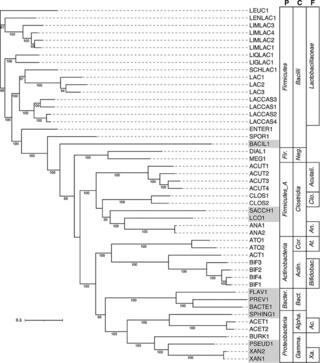
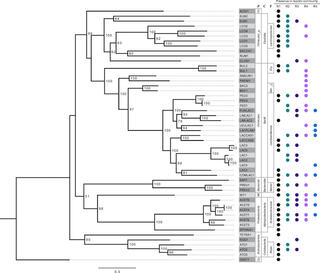
Metagenome-assembled genomes from a microbiome grown in dairy manure hydrolysate
Anaerobic microbiomes can be used to recover the chemical energy in agroindustrial and municipal wastes as useful products. Here, we report a total of 109 draft metagenome-assembled genomes from a bioreactor-fed carbohydrate-rich dairy manure hydrolysate.
Metagenomes and metagenome-assembled genomes from microbiomes metabolizing thin stillage from an ethanol biorefinery
Here, we report the metagenomes from five anaerobic bioreactors, operated under different conditions, that were fed carbohydrate-rich thin stillage from a corn starch ethanol plant. The putative functions of the abundant taxa identified here will inform future studies of microbial communities involved in valorizing this and other low-value agroindustrial residues.
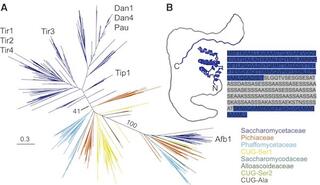
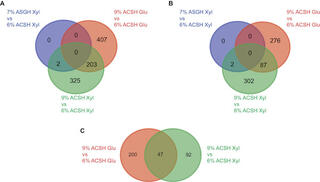
Functional divergence in a multi-gene family is a key evolutionary innovation for anaerobic growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
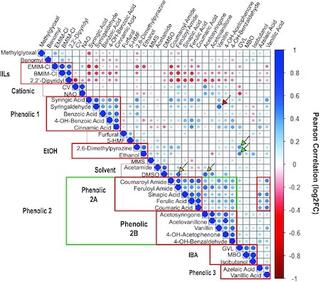
Comparative chemical genomic profiling across plant-based hydrolysate toxins reveals widespread antagonism in fitness contributions
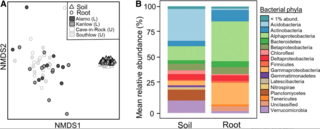
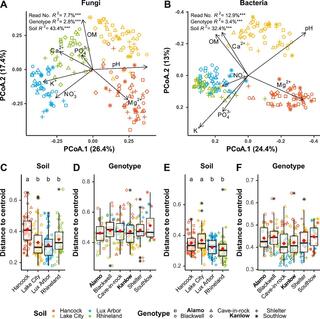
Host genotype controls ecological change in the leaf fungal microbiome
Leaf fungal microbiomes can be fundamental drivers of host plant success, as they contain pathogens that devastate crop plants and taxa that enhance nutrient uptake, discourage herbivory, and antagonize pathogens. We measured leaf fungal diversity with amplicon sequencing across an entire growing season in a diversity panel of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum).
Transcriptomic data sets for Zymomonas mobilis 2032 during fermentation of Ammonia Fiber Expansion (AFEX)-Pretreated corn stover and switchgrass hydrolysates
The transcriptomes of Zymomonas mobilis 2032 were captured during the fermentation of ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX)-pretreated corn stover and switchgrass hydrolysates containing different concentrations of glucose and xylose. RNA samples were collected when Z. mobilis was fermenting glucose or xylose.
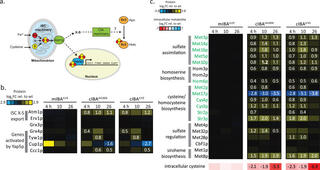
Comparative functional genomics identifies an iron-limited bottleneck in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with a cytosolic-localized isobutanol pathway
Metagenomes and metagenome-assembled genomes from microbial communities fermenting ultrafiltered milk permeate
Fermentative microbial communities can be utilized for the conversion of various agroindustrial residues into valuable chemicals. Here, we report 34 metagenomes from anaerobic bioreactors fed lactose-rich ultrafiltered milk permeate and 278 metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs).
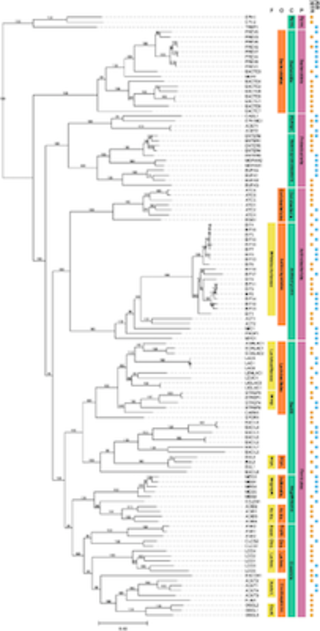
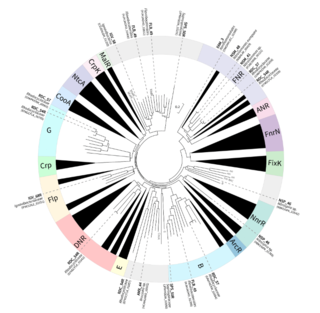
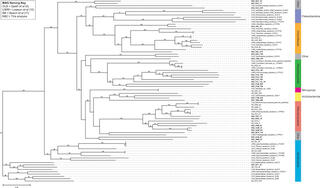
Exploring the meta-regulon of the CRP/FNR family of global transcriptional regulators in a partial-nitritation anammox microbiome
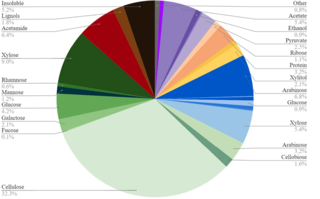
Utilization of lignocellulosic biofuel conversion residue by diverse microorganisms
Metagenomes from 25 low-abundance microbes in a partial nitritation anammox microbiome
Microbial communities using anammox bacteria to remove nitrogen are increasingly important in wastewater treatment. We report on 25 metagenome-assembled genomes of low-abundance microbes from a partial nitritation anammox bioreactor system that have not been described previously. These data add to the body of information about this important wastewater treatment system.