Overlooked Cooling Effects of Albedo
Background/Objective
The trapping of heat energy is a significant driver of global climate change. The absorbent nature of materials, such as asphalt, used for infrastructure can lead to an increase in temperature. When determining the value of various crop systems on our shared future, albedo is an often overlooked aspect of the calculation that may seriously impact climate patterns on this planet.
Approach
Using albedo measurements from seven experimental crops at a site in Michigan, researchers analyzed the effects of ecosystems as well as diurnal and seasonal changes on albedo. Using that data and existing research, they evaluated the shortcomings of current databases and methodologies.
Results
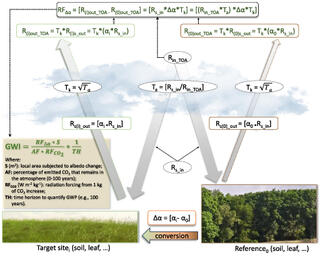
The paper shows that ecosystem types, as well as time of day and season, heavily impact the reflectivity of ground cover types, suggesting that new techniques need to be developed if albedo is to be properly considered in carbon credit programs and future policies.
Significance/Impacts
The research team proposes several research priorities based on their result, including forming a comprehensive global albedo database, developing regional systems of data collection sites, and enhancing current algorithms. They also emphasize the importance of constructing a system to calculate consequential global warming impact, in order to recognize and provide credits to landowners who actively contribute to climate regulation through sustainable management practices.