GLBRC Data Sets
Highlighted below are a variety of published studies that include data sets that might be of interest to the scientific community and have been deposited in online data repositories. Only data sets published in GLBRC-approved repositories following the FAIR Guiding Principles are highlighted. More information can be found on our guidelines page.
GLBRC Sustainability Data Catalog
This Data Catalog is a collection of data from GLBRC's Sustainability research carried out in Michigan and Wisconsin. The Data Catalog summarizes each data table in order to allow the GLBRC community to better understand the data that have been collected and encourage collaboration.
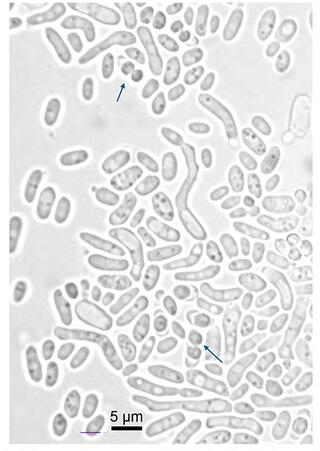
Vanderwaltozyma urihicola sp. nov., a yeast species isolated from rotting wood and beetles in a Brazilian Amazonian rainforest biome
Five yeast isolates belonging to a candidate for novel species were obtained from rotting wood and the gut of a passalid beetle larva in a site of Amazonian rainforest biome in Brazil.
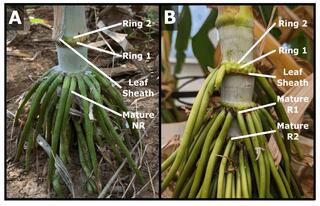
Bioenergy sorghum nodal root bud development: morphometric, transcriptomic and gene regulatory network analysis
Bioenergy sorghum’s large and deep nodal root system and associated microbiome enables uptake of water and nutrients from and deposition of soil organic carbon into soil profiles, key contributors to the crop’s resilience and sustainability. The goal of this study was to increase our understanding of bioenergy sorghum nodal root bud development.
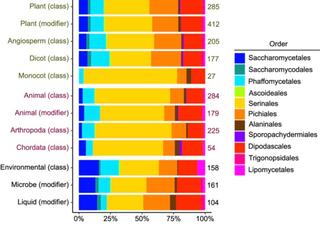
Exploring Saccharomycotina yeast ecology through an ecological ontology framework
Yeasts in the subphylum Saccharomycotina are found across the globe in disparate ecosystems. A major aim of yeast research is to understand the diversity and evolution of ecological traits, such as carbon metabolic breadth, insect association, and cactophily. This includes studying aspects of ecological traits like genetic architecture or association with other phenotypic traits.
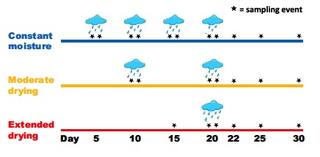
Rainfall events stimulate episodic associative nitrogen fixation in switchgrass
Associative N2 fixation (ANF) is wide- spread but poorly characterized, limiting our ability to estimate global inputs from N2 fixation. In some places, ANF rates are at or below detection most of the time but occasionally and unpredictably spiking to very high rates. Here we test the hypothesis that plant phenology and rainfall events stimulate ANF episodes.
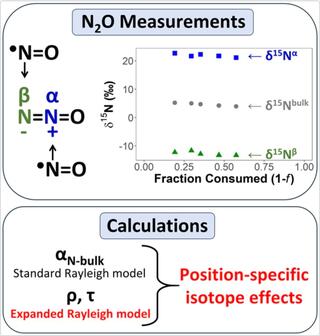
Position-specific kinetic isotope effects for nitrous oxide: a new expansion of the Rayleigh model
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas and the most significant anthropogenic ozone-depleting substance currently being emitted. A major source of anthropogenic N2O emissions is the microbial conversion of fixed nitrogen species from fertilizers in agricultural soils.
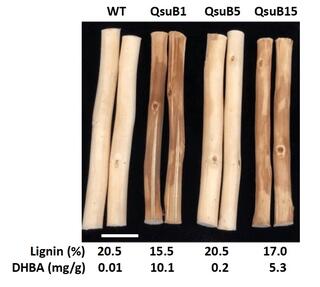
Genetic modification of the shikimate pathway to reduce lignin content in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) significantly impacts plant microbiomes
Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) is considered a sustainable biofuel feedstock, given its fast-impact growth, low input requirements, and high biomass yields. Improvements in bioenergy conversion efficiency of switchgrass could be made by reducing its lignin content.
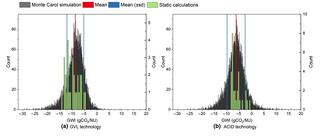
Uncertainties in greenhouse gas emission factors: a comprehensive analysis of switchgrass-based biofuel production
This study investigates uncertainties in greenhouse gas (GHG) emission factors related to switchgrass-based biofuel production in Michigan. Using three life cycle assessment (LCA) databases—US lifecycle inventory (USLCI) database, GREET, and Ecoinvent—each with multiple versions, we recalculated the global warming intensity (GWI) and GHG mitigation potential in a static calculation.
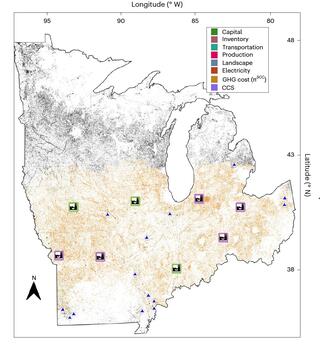
Large-scale spatially explicit analysis of carbon capture at cellulosic biorefineries
The large-scale production of cellulosic biofuels would involve spatially distributed systems including biomass fields, logistics networks and biorefineries. Better understanding of the interactions between landscape-related decisions and the design of biorefineries with carbon capture and storage (CCS) in a supply chain context is needed to enable efficient systems.
Genomic factors shaping codon usage across the Saccharomycotina subphylum
Codon usage bias, or the unequal use of synonymous codons, is observed across genes, genomes, and between species. It has been implicated in many cellular functions, such as translation dynamics and transcript stability, but can also be shaped by neutral forces.
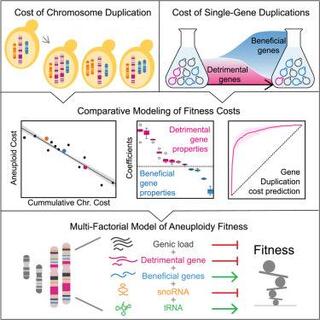
Comparative modeling reveals the molecular determinants of aneuploidy fitness cost in a wild yeast model
Although implicated as deleterious in many organisms, aneuploidy can underlie rapid phenotypic evolution. However, aneuploidy will be maintained only if the benefit outweighs the cost, which remains incompletely understood.
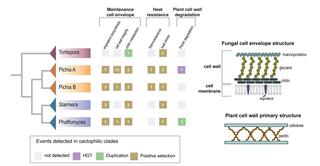
Diverse signatures of convergent evolution in cactus-associated yeasts
Many distantly related organisms have convergently evolved traits and lifestyles that enable them to live in similar ecological environments. However, the extent of phenotypic convergence evolving through the same or distinct genetic trajectories remains an open question.
Albedo of crops as a nature-based climate solution to global warming
Surface albedo can affect the energy budget and subsequently cause localized warming or cooling of the climate. When we convert a substantial portion of lands to agriculture, land surface properties are consequently altered, including albedo. Through crop selection and management, one can increase crop albedo to obtain higher levels of localized cooling effects to mitigate global warming.
Prediction of plant complex traits via integration of multi-omics data
The formation of complex traits is the consequence of genotype and activities at multiple molecular levels. However, connecting genotypes and these activities to complex traits remains challenging. Here, we investigate whether integrating genomic, transcriptomic, and methylomic data can improve prediction for six Arabidopsis traits.
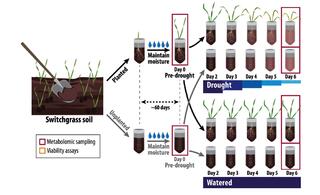
Disentangling plant- and environment-mediated drivers of active rhizosphere bacterial community dynamics during short-term drought
Mitigating the effects of climate stress on crops is important for global food security. The microbiome associated with plant roots, the rhizobiome, can harbor beneficial microbes that alleviate stress, but the factors influencing their recruitment are unclear.
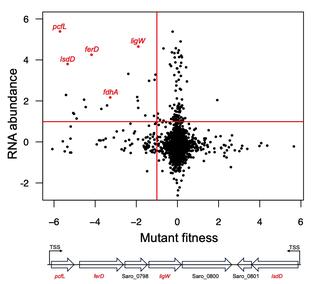
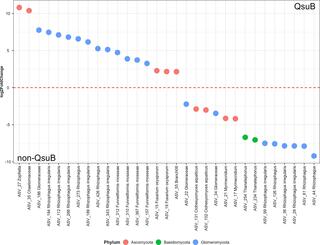
Catabolism of β-5 linked aromatics by Novosphingobium aromaticivorans
Aromatic compounds are an important source of commodity chemicals traditionally produced from fossil fuels. Aromatics derived from plant lignin can potentially be converted into commodity chemicals through depolymerization followed by microbial funneling of monomers and low molecular weight oligomers.
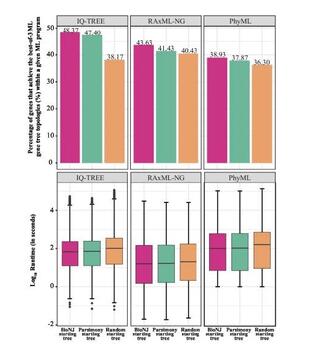
The influence of the number of tree searches on maximum likelihood inference in phylogenomics
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic inference is widely used in phylogenomics. As heuristic searches most likely find suboptimal trees, it is recommended to conduct multiple (e.g., ten) tree searches in phylogenetic analyses. However, beyond its positive role, how and to what extent multiple tree searches aid ML phylogenetic inference remains poorly explored.
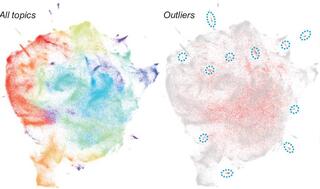
Assessing the evolution of research topics in a biological field using plant science as an example
Scientific advances due to conceptual or technological innovations can be revealed by examining how research topics have evolved. But such topical evolution is difficult to uncover and quantify because of the large body of literature and the need for expert knowledge in a wide range of areas in a field.
Expression in poplar of dehydroshikimate dehydratase induces transcriptional and metabolic changes in the phenylpropanoid pathway
Modification of lignin in feedstocks via genetic engineering aims to reduce biomass recalcitrance to facilitate efficient conversion processes. These improvements can be achieved by expressing exogenous enzymes that interfere with native biosynthetic pathways responsible for the production of the lignin precursors.
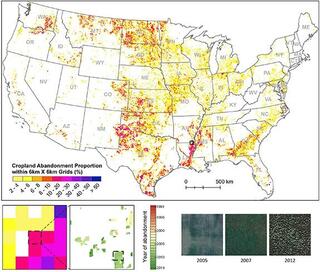
Cropland abandonment between 1986 and 2018 across the United States: spatiotemporal patterns and current land uses
Knowing where and when croplands have been abandoned or otherwise removed from cultivation is fundamental to evaluating future uses of these areas, e.g. as sites for ecological restoration, recultivation, bioenergy production, or other uses.



![Flow chart of methodology. Three types of omics data (genome [G], transcriptome [T], and methylome [M]) and phenotypic data for six traits were used in this study.](/sites/default/files/styles/small_320px_/public/data-and-tools-files/Shu%20paper%20compressed.jpg?itok=lRXZqmq8)