Vanderwaltozyma urihicola sp. nov., a yeast species isolated from rotting wood and beetles in a Brazilian Amazonian rainforest biome
F.B.M. Alvarenga et al "Vanderwaltozyma urihicola sp. nov., a yeast species isolated from rotting wood and beetles in a Brazilian Amazonian rainforest biome" International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2025) 75:006718 [DOI:10.1099/ijsem.0.006718]
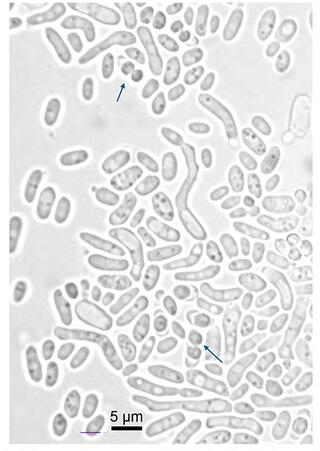
Five yeast isolates belonging to a candidate for novel species were obtained from rotting wood and the gut of a passalid beetle larva in a site of Amazonian rainforest biome in Brazil. Sequence analysis of the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS)-5.8S region and the D1/D2 domains of the large subunit rRNA gene showed that the isolates represent a novel species of the genus Vanderwaltozyma. The closest relative of the novel species is Vanderwaltozyma huisunica. These species differs due to 44 nt substitutions and 21 indels in the sequences of the ITS region, as well as by 15 substitutions and four indels in the sequences of the D1/D2 domains. A phylogenomic analysis of the Vanderwaltozyma species with genomes sequenced showed that this novel species is an outgroup to the other species of this genus. We propose the name Vanderwaltozyma urihicola sp. nov. (CBS 18107(T), MycoBank MB 856975) to accommodate these isolates. The species is homothallic, producing one to two ascospores per ascus. The habitat of V. urihicola is rotting wood in the Brazilian Amazonian rainforest biome.
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the gene sequences of the ITS region and D1/D2 domains of the large subunit rRNA gene of V. urihicola sp. nov. UFMG-CM-Y7006 are OM095316 and OM095314, respectively. The Whole Genome Shotgun project of strain V. urihicola sp. nov. UFMG-CM-Y7006 has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under accession JBGIYV000000000.