Cu-catalyzed oxidation cleaves C–C bonds in lignin-derived oligomers for biological funneling
Background/Objective
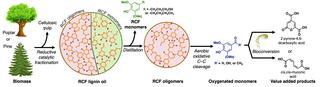
Most methods for lignin deconstruction cleave carbon–oxygen bonds, resulting in suboptimal yields of aromatic monomers and formation of oligomers with intact carbon–carbon bonds that limit the yield of valorized products. This work demonstrates a copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidation process that converts oligomeric “waste” derived from reductive catalytic fractionation (RCF) of woody biomass into aromatic monomers. The resulting monomers are used as feedstock for biological funneling into bioproducts.
Approach
Cu-catalyzed aerobic oxidation was used to convert RCF oligomers from poplar and pine biomass using an O2-permeable flow reactor. An engineered strain of Pseudomonas putida (KT2440) funneled the mixtures of oxidized aromatic monomers from pine to cis,cis-muconic acid (muconate) and from poplar to 2-pyron-4,6-dicarboxylic acid (PDC).
Results
Monomer yields from RCF oligomers were higher or comparable to those from the best pretreatment lignin sources. Collectively, the pairing of RCF and oxidative C-C cleavage produced a total monomer yield of 33 wt% and 63 wt% aromatic monomers from pine and poplar RCF oils respectively. Muconate production from pine-derived oils produced a yield of 127 mol% (±11%), suggesting conversion of additional unknown compounds. PDC production from poplar-derived oils produced 57 mol% (±2%) yield.
Significance/Impacts
This catalytic oxidation process capable of cleaving carbon-carbon bonds enables less-valuable oligomers to be converted efficiently to aromatic monomers that readily undergo bioconversion to valuable products. The process uses inexpensive Cu salts and does not require protection of phenols prior to the reaction. This collaboration between the Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory integrates chemical and biological processes to maximize yields of bioproducts derived from lignin feedstocks.
Omolabake, S., et al. (n.d.). Cu-Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidative C─C Cleavage in Lignin-Derived Oligomers and Biological Funneling of the Monomeric Products. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, n/a, e15588. [DOI:10.1002/anie.202515588]