MarK, a Novosphingobium aromaticivorans kinase required for catabolism of multiple aromatic monomers
B.W. Hall et al. "MarK, a Novosphingobium aromaticivorans kinase required for catabolism of multiple aromatic monomers" Journal of Biological Chemistry (2025) 301:110606 [DOI:10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110606]
The aromatic compounds used in a variety of industrial products are currently obtained from nonrenewable petroleum sources. Alternatively, the plant polymer lignin is an abundant renewable source of aromatics, and its depolymerization generates a variety of products that can include acetovanillone, a vanillin derivative containing an acetyl side chain. The Alphaproteobacterium Novosphingobium aromaticivorans DSM12444 can metabolize several chemically modified aromatics in deconstructed lignin, but not acetovanillone. In this work, adaptive laboratory evolution identified a single amino acid
change in the previously uncharacterized gene product Saro_1862 that is necessary and sufficient for N. aromaticivorans growth with acetovanillone as a sole growth substrate, as well as other aromatic monomers not metabolized by wild-type cells. We show that a glutamate (E) to lysine (K) substitution at amino acid residue 16 of Saro_1862 results in a ~1600-fold increase in the rate of ATP-dependent acetovanillone phosphorylation. We also find that recombinant Saro_1862 E16K phosphorylates several other aromatic compounds in vitro, defining the first reported catalytic activity for the widespread
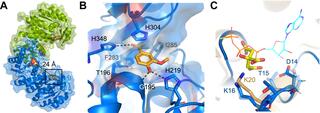
UPF0261 protein domain contained in Saro_1862. Thus, we propose naming Saro_1862 MarK, for multiple aromatic kinase. A 1.57 Å crystal structure of MarK E16K predicts that the E16K substitution lies in a potential ATP binding site, suggesting how this amino acid change increased catalytic activity. A search for homologs of MarK and other proteins required for acetovanillone degradation predicts that this pathway for aromatic metabolism exists throughout the bacterial phylogeny.
The atomic coordinates and structure factors for MarK (code 9MPY) have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (http://wwpdb.org/). Frame data have been deposited in (https://www.proteindiffraction.org). All other data described in the manuscript are provided in the manuscript or in Supporting Information.